Durabolin, more commonly known among bodybuilders as Nandrolone Phenylpropionate, or just NPP, is a close relative of the popular steroid Deca Durabolin. However, due to the fact that for a long time NPP was hard to find and the available servings were not convenient, this steroid was rarely used by anybody. Luckily, in recent years underground labs developed durabolin in all kinds of dosages, making it more accessible and practical for use. Therefore, this steroid deserves a special attention, because it is more than just Deca Durabolin with a different ester.
Contents
History
 Since NPP and deca share the same active substance – nandrolone, their history is very closely linked together. Few people know that nandrolone as such was developed in 1957, and the most popular version of this steroid was actually the one with the phenylpropionate ester attached to it. Nevertheless, a new version with the decanoate ester has been released in 1962, and it was commercially named Deca Durabolin. Thanks to some considerable advantages in convenience of use it became more popular than the phenylpropionate form of nandrolone. As a result, deca became one of the most widely used steroids of all times, whilst NPP has become a rare anabolic androgenic steroid (AAS).
Since NPP and deca share the same active substance – nandrolone, their history is very closely linked together. Few people know that nandrolone as such was developed in 1957, and the most popular version of this steroid was actually the one with the phenylpropionate ester attached to it. Nevertheless, a new version with the decanoate ester has been released in 1962, and it was commercially named Deca Durabolin. Thanks to some considerable advantages in convenience of use it became more popular than the phenylpropionate form of nandrolone. As a result, deca became one of the most widely used steroids of all times, whilst NPP has become a rare anabolic androgenic steroid (AAS).
Still, underground labs were able to eliminate one of the major disadvantages of NPP by making durabolin available in different servings. This allowed NPP to find its place in modern bodybuilding, for its shorter ester also has some advantages to offer, and it is becoming more and more popular.
Nandrolone in Medicine
Initially, nandrolone was used in the treatment of a huge variety of diseases and conditions, where it proved itself to be effective. Just to list some of these, nandrolone can be beneficial for osteoporosis, breast cancer, burns, injury healing, and growth deficiency in children. In fact, clinical studies showed that nandrolone produced considerable regressions in women with carcinomas.
What’s more, considering the great potential of adding lean mass, nandrolone was used particularly often to prevent muscle degeneration caused by atrophy or wasting syndromes related to HIV/AIDS, chronic debilitating diseases, major surgery, and severe trauma.
However, over the years, the US FDA has been shortening the list of diseases where nandrolone’s use is allowed for treatment. These days, nandrolone is only prescribed to treat anemic patients and those suffering wasting syndromes, especially HIV/AIDS related.
Interestingly, there is yet another medical benefit that is often reported by those using nandrolone – immune system enhancement. According to anecdotal evidence, nandrolone greatly improves the immune system, and it is therefore often employed as a supporting agent.
Regarding the medical use of deca durabolin or NPP, deca was always the most popular of the two, since it allows to make less frequent injections, which is a very important aspect for most patients. Nonetheless, NPP has the advantage of a faster action that is so necessary in cases of clinical emergencies, where immediate results are needed.
Profile
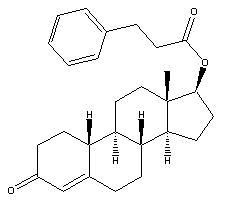
NPP Chemical Structure
Nandrolone is an anabolic steroid that belongs to the 19-nortestosterone family. As a matter of fact, it is very similar to testosterone, with only one difference – it lacks one carbon at the 19th position. Hence the name of the nandrolone related steroids family, which are also frequently called 19-nor compounds.
As a consequence of this structural difference, unlike testosterone, which is converted into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the 5-alpha reductase enzyme, nandrolone transforms into a weaker androgen – dihydronandrolone. This does not allow the stronger DHT bind to the androgen receptors, causing considerable suppression of natural testosterone production. Therefore, it is always recommended to use nandrolone based steroids in conjunction with testosterone.
Regarding the aromatization of nandrolone, it is not significant enough to be an issue. In fact, it has a very low estrogen conversion rate, which is according to some studies five times slower than that of testosterone. Consequently, when reasonable dosages are taken, estrogenic side effects are pretty manageable, especially with such aromatase inhibitors (AI) as Aromasin.
Another important property of nandrolone to keep in mind, is its progestational activity. Since this compound has a strong binding affinity to the progesterone receptors, progestine related side effects may occur. This is a very noteworthy moment because these effects resemble very much those of estrogen. In case these effects do take place, such drugs as Proviron and Nolvadex can be helpful.
All in all, just like testosterone, nandrolone is produced naturally within the human body, but it has a different set of properties. It is slightly more anabolic than testosterone and considerably less androgenic. Therefore, those looking for a steroid with less androgenic effects than testosterone, should definitely consider nandrolone.
Additional benefits of Durabolin
 Among many other conditions, nandrolone was used to treat anemia. The reason for that is its ability to boost red blood cell (RBC) production, which can also be very beneficial for bodybuilders, who need more RBC to deliver the oxygen to the muscles.
Among many other conditions, nandrolone was used to treat anemia. The reason for that is its ability to boost red blood cell (RBC) production, which can also be very beneficial for bodybuilders, who need more RBC to deliver the oxygen to the muscles.
Moreover, it is known that nandrolone can increase collagen production in the body, so it can be a great help for joints. Hence its popular use for joint pain relief, which is not a reasonable thing to do, since this AAS has a different purpose. In addition to this, nandrolone can considerably increase bone mineral content, making a good combination with the enhanced collagen synthesis.
Nitrogen retention is another huge benefit of nandrolone. As it is well known, nitrogen retention is very important for lean mass preservation, which makes nandrolone a perfect steroid for cutting and adding definition to the musculature.
NPP vs. Deca Durabolin
 Both of these steroids are based on the same active substance – nandrolone. However, even though they share most of nandrolone’s benefits and drawbacks, NPP and Deca Durabolin have different esters that bring along certain differences. NPP has the short acting phenylpropionate ester attached to it, whilst Deca Durabolin has the considerably longer acting decanoate ester. In spite of the fact that the esters are supposed to impact exclusively the release rates of the active substance, these two steroids have further reaching differences in their action that give different applications for each of them.
Both of these steroids are based on the same active substance – nandrolone. However, even though they share most of nandrolone’s benefits and drawbacks, NPP and Deca Durabolin have different esters that bring along certain differences. NPP has the short acting phenylpropionate ester attached to it, whilst Deca Durabolin has the considerably longer acting decanoate ester. In spite of the fact that the esters are supposed to impact exclusively the release rates of the active substance, these two steroids have further reaching differences in their action that give different applications for each of them.
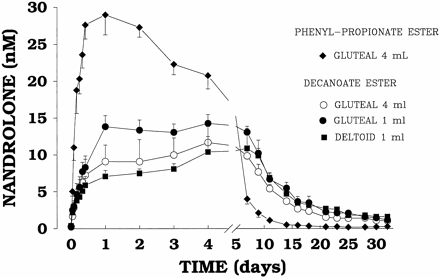
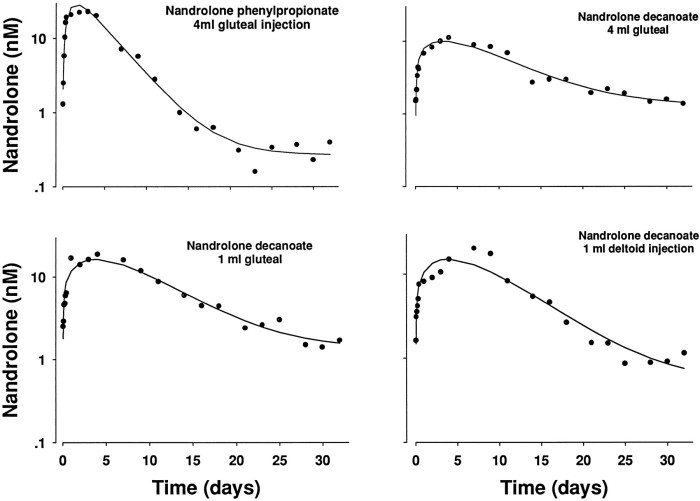
The shorter ester of NPP is both an advantage, and a disadvantage. On one side, due to its short half-life, more injections are needed when using it in comparison to deca – 2-3 injections per week vs. 1 injection per week. On the other hand, the short half-life makes NPP a faster acting steroid than deca, which allows to run shorter cycles with the same results. For instance, an average deca cycle will last 14-16 weeks, and a longer recovery time will be needed as a result of such a long cycle. Whereas 10 weeks are plenty in the case of NPP, which requires less recovery time.
Furthermore, the long ester of deca delays the action of this steroid, making some kick-starting orals necessary when cycling it. Whereas NPP starts acting much faster, making it possible to use less AAS during a cycle, since no kick-starters are necessary. This also means that NPP will clear out of the system much faster than deca; according to some studies, it clears out of the body twice as fast.
Another advantage of NPP, more anecdotal in nature, is that it causes less water retention. In fact, it is a trait often observed in steroids with shorter esters, and NPP is not an exclusion. Bodybuilders report having considerably less bloating and water retention when they use NPP compared to deca. Most probably, this fact is related to the fact that usually less mass gains are achieved with NPP than with deca.
 Nonetheless, apart from the obvious differences in ester lengths and their effects, NPP has one disadvantage that is mentioned quite often in the bodybuilding community. According to these rumors, NPP injections are very painful, or at least they are definitely more painful than deca injections. However, this pain is not serious enough as to draw back a potential user – it is rather uncomfortable, than truly painful.
Nonetheless, apart from the obvious differences in ester lengths and their effects, NPP has one disadvantage that is mentioned quite often in the bodybuilding community. According to these rumors, NPP injections are very painful, or at least they are definitely more painful than deca injections. However, this pain is not serious enough as to draw back a potential user – it is rather uncomfortable, than truly painful.
Finally, NPP may not be the optimal steroid for some individuals due to economic reasons. Although it has a reasonable price on the black market, the frequent injections require bigger amounts of this AAS, which increases the overall expenses.
Side Effects
 Nandrolone, especially the phenylpropionate version, is known to be a steroid with relatively mild side effects. As mentioned previously, estrogenic side effects are not common and they are easily manageable. Furthermore, due to moderate androgenic activity, compared to other AAS durabolin gives less androgenic side effects, such as oily skin, body/facial hair growth, male pattern baldness, etc.
Nandrolone, especially the phenylpropionate version, is known to be a steroid with relatively mild side effects. As mentioned previously, estrogenic side effects are not common and they are easily manageable. Furthermore, due to moderate androgenic activity, compared to other AAS durabolin gives less androgenic side effects, such as oily skin, body/facial hair growth, male pattern baldness, etc.
However, in spite of the moderate estrogen conversion rate, NPP can be suppressive. Therefore, such agents as HCGenerate ES and Clomid are recommended at the end of the cycle and during PCT. They will boost natural testosterone production, helping the body recover faster.
All in all, NPP has the same kind of side effects as deca durabolin, with the only difference that these are milder. Moreover, the prominence of these side effects will be dose dependent; therefore, if moderate dosages are used, NPP’s side effects should not be too much of a concern.
Female athletes
 Durabolin should be the preferred option for women who are choosing a nandrolone based steroid. Moderate androgenic effects and the short acting ester make the use of NPP relatively safe. Unlike deca, which will take weeks to clear out of the body in case virilization symptoms take place, NPP will be depleted in a matter of days. This simplifies the control of hormonal levels.
Durabolin should be the preferred option for women who are choosing a nandrolone based steroid. Moderate androgenic effects and the short acting ester make the use of NPP relatively safe. Unlike deca, which will take weeks to clear out of the body in case virilization symptoms take place, NPP will be depleted in a matter of days. This simplifies the control of hormonal levels.
Interestingly, unlike men, who do NPP injections 2-3 times per week, women need to do just one. It is best not to exceed 50-60 milligrams (mgs) per week. This amount will be plenty enough to make considerable gains of high quality muscle mass, and avoid most of the side effects.
Dosages and Use
The average dose of NPP for men is 300 milligrams (mgs) per week. Hence, it can be either used twice a week at 150 mgs per injection, or three times per week with 100mgs injections. There are no major differences between these two injection schedules, so it is mostly a matter of taste and individual approaches to cycles. Regarding cycle duration, thanks to the short acting ester 10 weeks are plenty for good results.
Stacking wise, durabolin is most frequently combined with short ester steroids, such as testosterone propionate and boldenone acetate. Furthermore, it can also be successfully stacked with such orals as winstrol and anavar. All of these steroids are used in short cycles, which perfectly fits into the short cycle concept of NPP. Nonetheless, durabolin can also be used in longer cycles because its mild side effect allow to do so without jeopardizing one’s health.
Nandrolone phenylpropionate is a slow and steady mass gainer. Due to its nitrogen retaining properties, it gives a very lean musculature, which is more keepable after ending a cycle. This, together with reduced water retention, makes this steroid a preferred choice for cutting and pre-contest preparation. On the other hand, it is worth mentioning that deca durabolin is used mostly for bulking purposes.
Half-life
Durabolin’s half life is roughly 6 days, which is a relatively long period compared to many other steroids.
Conclusion
Although some people may consider NPP just as Deca Durabolin with a shorter ester, it is a very different steroid with its own set of properties. It is a faster acting and milder version of deca, which is also somewhat safer in terms of side effects. Therefore, NPP will be a good addition to any steroid stack, especially if it is a cutting one.
Evolutionary.org: “Nandrolone phenylpropionate (NPP)”.
U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, HIV/AIDS: “HIV wasting syndrome”.
© 2015 iSARMS.com, LLC. All rights reserved.





